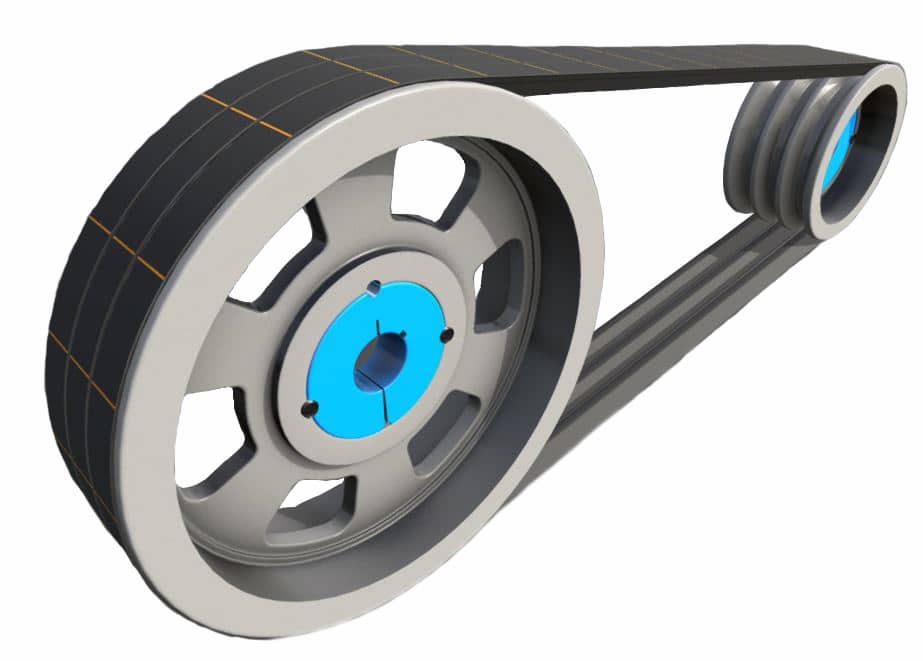
Product Description
V Belt Pulley with ISO9001 (SPA, SPB, SPC, SPZ)
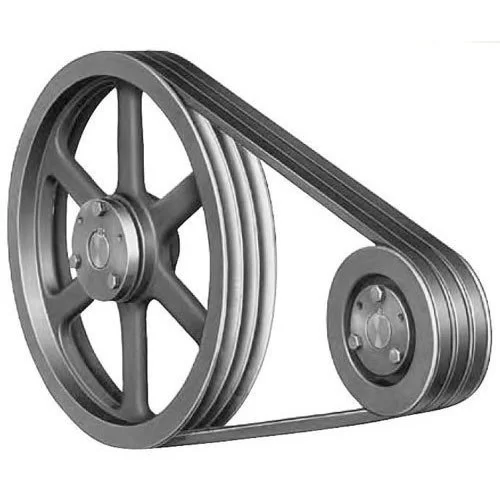
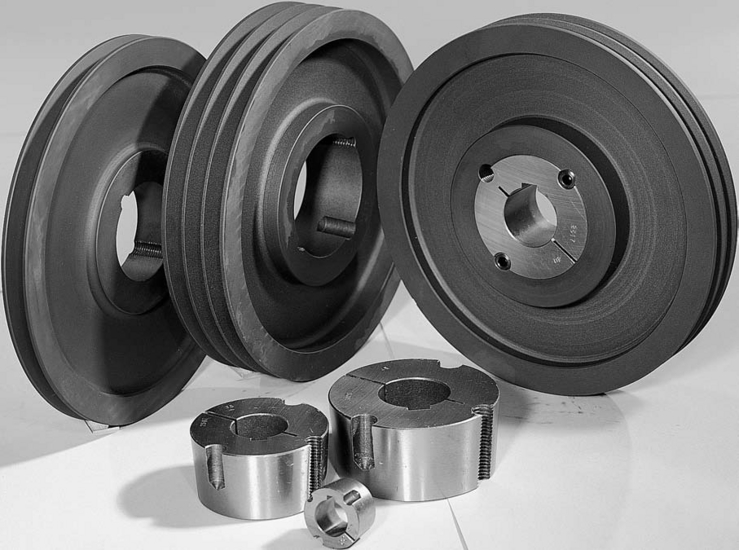
1. V-Pulley
Taper Bore
SPZ SPA CHINAMFG SPC
2. V-Pulley
Stock Bore
SPZ SPA CHINAMFG SPC
3. V-Pulley
Adjustable Speed
TB-1 TB-2 SB-1 SB-2
4. V-Pulley
Multi-Wedged
J L M
| 50 – 1 x SPZ – 1008 rü 15 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 56 – 1 x SPZ – 1008 rü 15 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 60 – 1 x SPZ – 1008 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 63 – 1 x SPZ – 1108 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 67 – 1 x SPZ – 1108 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 71 – 1 x SPZ – 1108 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 75 – 1 x SPZ – 1108 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 80 – 1 x SPZ – 1210 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 85 – 1 x SPZ – 1210 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 90 – 1 x SPZ – 1210 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 95 – 1 x SPZ – 1210 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 100 – 1 x SPZ – 1210 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 106 – 1 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 112 – 1 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 118 – 1 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 125 – 1 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 132 – 1 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 140 – 1 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 150 – 1 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 160 – 1 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 170 – 1 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 180 – 1 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 190 – 1 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 200 – 1 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 224 – 1 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 250 – 1 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 280 – 1 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 315 – 1 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 355 – 1 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 400 – 1 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 500 – 1 x SPZ – 2517 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 50 – 2 x SPZ – 1008 rü 26 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 56 – 2 x SPZ – 1108 rü 26 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 60 – 2 x SPZ – 1108 rü 26 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 63 – 2 x SPZ – 1108 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 67 – 2 x SPZ – 1108 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 71 – 2 x SPZ – 1108 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 75 – 2 x SPZ – 1210 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 80 – 2 x SPZ – 1210 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 85 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 90 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 95 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 100 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 106 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 112 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 118 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 125 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 132 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 140 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 150 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 160 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 170 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 180 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 190 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 200 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 224 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 250 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 280 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 315 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 355 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 400 – 2 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 450 – 2 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 500 – 2 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 63 – 3 x SPZ – 1108 rü 17 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 67 – 3 x SPZ – 1108 rü 17 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 71 – 3 x SPZ – 1108 rü 17 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 75 – 3 x SPZ – 1210 rü 14 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 80 – 3 x SPZ – 1210 rü 14 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 85 – 3 x SPZ – 1610 rü 14 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 90 – 3 x SPZ – 1610 rü 14 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 95 – 3 x SPZ – 1610 rü 14 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 100 – 3 x SPZ – 1610 rü 14 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 106 – 3 x SPZ – 1610 rü 14 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 112 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 118 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 125 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 132 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 140 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 150 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 160 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 170 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 180 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 190 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 200 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 224 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 250 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 280 – 3 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 315 – 3 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 355 – 3 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 400 – 3 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 450 – 3 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 500 – 3 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 630 – 3 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 63 – 4 x SPZ – 1108 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 67 – 4 x SPZ – 1108 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 71 – 4 x SPZ – 1108 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 75 – 4 x SPZ – 1210 rü 26 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 80 – 4 x SPZ – 1210 rü 26 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 85 – 4 x SPZ – 1610 rü 26 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 90 – 4 x SPZ – 1610 rü 26 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 95 – 4 x SPZ – 1610 rü 26 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 100 – 4 x SPZ – 2012 rü 20 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 106 – 4 x SPZ – 2012 rü 20 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 112 – 4 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 118 – 4 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 125 – 4 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 132 – 4 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 140 – 4 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 150 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 160 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 170 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 180 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 190 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 200 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 224 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 250 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 280 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 315 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 355 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 400 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 450 – 4 x SPZ – 3571 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 500 – 4 x SPZ – 3571 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 630 – 4 x SPZ – 3030 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 800 – 4 x SPZ – 3030 e.b. | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 85 – 5 x SPZ – 1610 rü 38 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 90 – 5 x SPZ – 1610 rü 38 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 95 – 5 x SPZ – 1610 rü 38 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 100 – 5 x SPZ – 2012 rü 32 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 106 – 5 x SPZ – 2012 rü 32 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 112 – 5 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 118 – 5 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 125 – 5 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 132 – 5 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 140 – 5 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 150 – 5 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 160 – 5 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 180 – 5 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 200 – 5 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 224 – 5 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 250 – 5 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 280 – 5 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 315 – 5 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 355 – 5 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 400 – 5 x SPZ – 3571 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 450 – 5 x SPZ – 3571 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 500 – 5 x SPZ – 3030 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 630 – 5 x SPZ – 3030 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 100 – 6 x SPZ – 2012 rü 44 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 106 – 6 x SPZ – 2012 rü 44 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 112 – 6 x SPZ – 2012 rü 44 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 118 – 6 x SPZ – 2517 rü 31 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
Choose GOODLUCK(TAI)
1. Our company boasts a combination of research and development, production and sales with highly professional capabilities.
2. Our company produces the pulley with the following: Drive can mitigate impact load; Transmission smooth operation, low noise, low vibration; Transmission of simple structure, easy to adjust; Drive for the manufacture and installation precision of pulley, unlike meshing transmission strictly; It has the function of overload protection; Transmission center distance of 2 axis adjusting range is larger.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Certification: | ISO |
|---|---|
| Pulley Sizes: | All |
| Manufacturing Process: | Casting |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How do belt pulleys affect the performance of woodworking and milling machines?
Belt pulleys have a significant impact on the performance of woodworking and milling machines. They play a crucial role in power transmission, speed control, and overall functionality of these machines. Here’s a detailed explanation of how belt pulleys affect the performance of woodworking and milling machines:
1. Power Transmission: Belt pulleys are essential for power transmission in woodworking and milling machines. They connect the motor or engine to various components, such as the cutting tools, spindles, or feed mechanisms. The rotation of the pulleys transfers power from the motor to the driven components, enabling them to perform their cutting, shaping, or drilling functions. The efficiency and effectiveness of power transmission through the belt pulleys directly impact the overall performance of the machine.
2. Speed Control: Belt pulleys provide speed control in woodworking and milling machines. By using pulleys of different sizes or incorporating variable speed pulley systems, the rotational speed of the driven components can be adjusted. This allows operators to customize the speed based on the specific material being worked on and the desired cutting or milling results. Speed control provided by belt pulleys ensures precision, accuracy, and optimal performance in woodworking and milling operations.
3. Torque Conversion: Belt pulleys also play a crucial role in torque conversion. Torque refers to the rotational force produced by the motor or engine. In woodworking and milling machines, belt pulleys with different diameters can be used to convert the torque generated by the motor into the appropriate torque required by the cutting tools or spindles. This torque conversion ensures that the machine can handle different types of materials and cutting operations effectively, enhancing overall performance.
4. Belt Tension and Stability: Proper tension and stability of the belts running on the pulleys are essential for the performance of woodworking and milling machines. The tension in the belts needs to be adjusted to ensure optimal power transmission and prevent slipping or belt damage. Belt pulleys are designed to maintain the appropriate tension and stability of the belts, ensuring smooth and consistent operation of the machine. This contributes to the accuracy, reliability, and safety of woodworking and milling processes.
5. Tooling and Cutter Compatibility: Belt pulleys can affect the performance of woodworking and milling machines by influencing tooling and cutter compatibility. Different cutting tools and milling cutters require specific rotational speeds and power transmission capacities. The selection of appropriate pulleys and belt arrangements ensures compatibility between the machine’s power transmission system and the cutting tools or milling cutters being used. This compatibility is crucial for achieving desired cutting results, prolonging tool life, and maximizing machine performance.
6. Noise and Vibration: Belt pulleys can impact the noise and vibration levels of woodworking and milling machines. Proper alignment and balancing of the pulleys are essential to minimize vibration and noise generated during operation. Excessive noise and vibration can affect the precision of cuts or milling operations and lead to accelerated wear and tear of machine components. Well-designed and properly maintained belt pulleys contribute to reduced noise and vibration, enhancing the overall performance and operator comfort.
7. Maintenance and Serviceability: Belt pulleys in woodworking and milling machines are designed for easy maintenance and serviceability. They allow for straightforward belt replacement, adjustment, or pulley inspection, ensuring that the machine can be properly maintained and serviced. This contributes to the longevity, reliability, and uninterrupted operation of the woodworking and milling machines.
In summary, belt pulleys have a significant impact on the performance of woodworking and milling machines. They enable power transmission, speed control, torque conversion, and stability of belts. Belt pulleys affect tooling and cutter compatibility, noise and vibration levels, as well as the maintenance and serviceability of the machines. By selecting appropriate pulleys, maintaining proper belt tension, and ensuring pulley alignment, woodworking and milling machines can achieve optimal performance, accuracy, and efficiency in various cutting and shaping tasks.

What types of belts are commonly used with belt pulleys?
Several types of belts are commonly used in conjunction with belt pulleys for power transmission in various applications. The choice of belt depends on factors such as the specific requirements of the machinery, the desired power transmission characteristics, environmental conditions, and the type of pulley system being used. Here are some of the most commonly used types of belts:
1. V-Belts: V-belts, also known as Vee belts, are one of the most widely used types of belts with belt pulleys. They have a trapezoidal cross-section and typically feature a fabric cover and a rubber-like compound. V-belts are known for their high grip and power transmission capabilities, making them suitable for applications with moderate to high loads and speeds. They are commonly used in industries such as automotive, industrial machinery, and HVAC systems.
2. Timing Belts: Timing belts, also called synchronous belts, have toothed profiles on the inner side that engage with corresponding teeth on the pulley. This toothed design provides precise power transmission and prevents slippage. Timing belts are commonly used in applications that require precise synchronization of shafts and accurate positioning, such as in robotics, printing machinery, and automotive engines.
3. Flat Belts: Flat belts have a rectangular cross-section and are typically made of materials such as rubber, fabric, or synthetic compounds. They are flexible and can be easily customized to various lengths. Flat belts are commonly used in applications where high speeds and low power transmission requirements are present, such as in conveyor systems, textile machinery, and packaging equipment.
4. Round Belts: Round belts, also known as round O-ring belts, are circular belts made of materials such as rubber or urethane. They are flexible and can be easily joined to form endless loops. Round belts are commonly used in applications that require a lightweight and flexible power transmission solution, such as in small appliances, office equipment, and material handling systems.
5. Ribbed Belts: Ribbed belts, also called multi-rib belts or serpentine belts, have a ribbed or grooved design on the inner side. These ribs engage with corresponding grooves on the pulley, providing increased contact area and improved power transmission efficiency. Ribbed belts are commonly used in automotive engines, where they drive multiple accessories such as alternators, power steering pumps, and air conditioning compressors.
6. Variable Speed Belts: Variable speed belts, also known as adjustable speed belts or link belts, are made of individual links or segments that can be easily connected or disconnected to adjust the belt length. This allows for stepless speed variation and flexibility in power transmission. Variable speed belts are commonly used in applications where speed adjustment is required, such as in milling machines, woodworking equipment, and industrial conveyors.
These are just a few examples of the types of belts commonly used with belt pulleys. Each type of belt has its own unique characteristics and is suitable for specific applications based on factors such as load capacity, speed requirements, precision, and environmental conditions. The selection of the appropriate belt is crucial to ensure efficient and reliable power transmission in the machinery and equipment utilizing belt pulleys.

How does a belt pulley function in power transmission?
A belt pulley plays a crucial role in power transmission by enabling the transfer of rotational motion and torque between rotating shafts. It functions as a mechanical device that connects the driving shaft to the driven shaft through a belt or a rope. The rotational motion of the driving shaft is transmitted to the driven shaft via the belt pulley, allowing power to be transferred from one shaft to another. Here’s a detailed explanation:
A belt pulley functions in power transmission through the following process:
- The driving shaft, which is typically connected to a motor or an engine, rotates and generates rotational motion and torque.
- The belt pulley is mounted on the driving shaft, and its grooved rim is designed to engage with a belt or a rope.
- A belt or a rope is wrapped around the groove of the belt pulley, creating a secure connection between the pulley and the belt.
- As the driving shaft rotates, the belt or rope, in contact with the grooved rim of the pulley, starts to move.
- The movement of the belt or rope causes the belt pulley to rotate.
- Since the belt pulley is connected to the driven shaft, which is the output shaft of the system, the rotational motion of the pulley is transferred to the driven shaft.
- Consequently, the driven shaft starts to rotate at the same speed and direction as the driving shaft.
- The rotational motion and torque generated by the driving shaft are effectively transmitted to the driven shaft through the belt pulley and the belt or rope.
It’s important to note that the design and configuration of the belt pulley, along with the belt or rope, are essential for efficient power transmission. The groove profile of the pulley should match the belt or rope profile to ensure proper engagement and prevent slippage. The tension in the belt or rope should be appropriately adjusted to maintain a secure connection between the pulley and the belt. Additionally, the size and ratio of the pulleys connected by the belt can be adjusted to control the speed and torque output, providing flexibility in power transmission.
In summary, a belt pulley functions in power transmission by connecting the driving shaft to the driven shaft through a belt or a rope. It transfers the rotational motion and torque generated by the driving shaft to the driven shaft, allowing power to be transmitted between the two shafts. The design, configuration, and tensioning of the belt and the pulley are crucial for efficient and reliable power transmission in mechanical systems.


editor by CX
2024-04-19