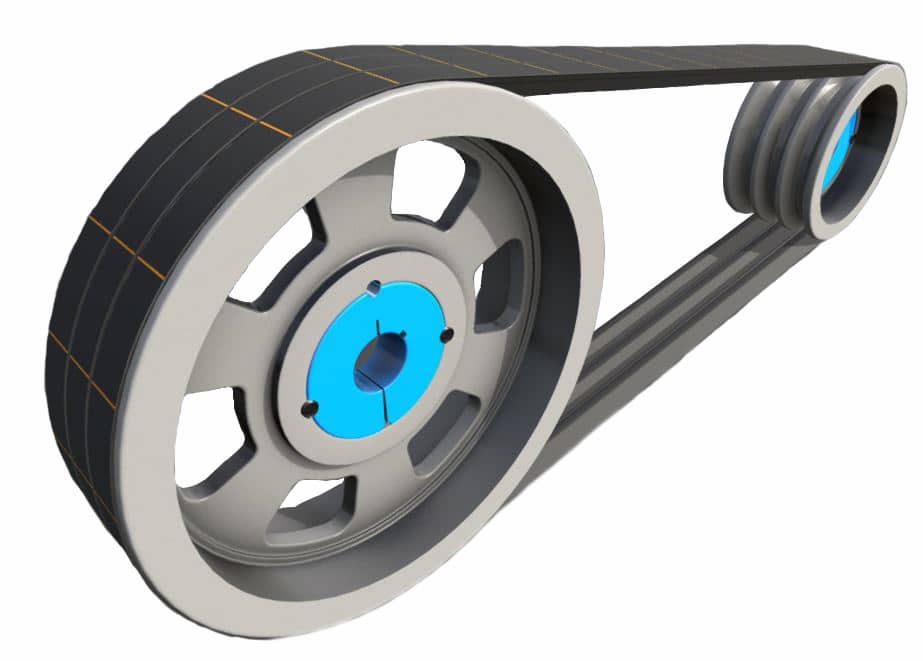
Product Description
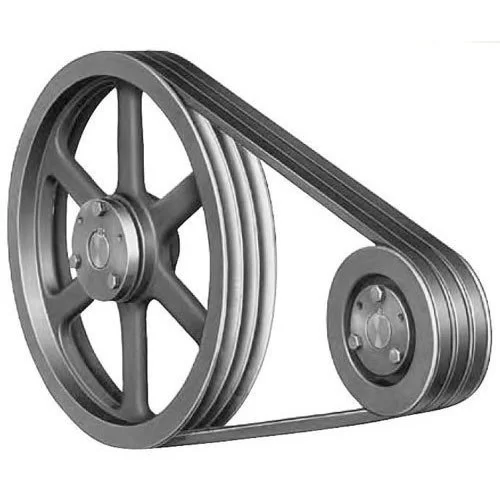
Motorcycle Drive Face for Vespa125 PIAGGIO 2612B-IZ35-0001
Product Specification:
| Product Name: | Drive Face |
| Item No: | 2612B-IZ35-0001 |
| Model: | Piaggio |
| Size: | Normal Standard |
| Quantity guarantee: | 12 months(Testing before delivery |
| Delivery: | Within 30-45 days after deposit received |
| Packing: | Neutral packing or As customer requirement,blank packing |
| Payment Term: | T/T |
Related Products:
We are the leading exporter of Motorcycle Parts from China. We have all kinds of spare parts.
| Brand | Available mode |
| Honda | SCR100, Space110, PCX125, PCX150, SH125, SH150, Vision 110, Air Blade 110, Air Blade 125, Spacy Alpha, CBF150, Fizy125, Elite125, Activa S, CB125E, CB125F, CG125, Today 50, Wave110, Wave125, Click110, Click125, XR125, XR150, Vario, CBR150, CBR250, CBR400, Beat, Stream etc. |
| Piaggio | LX50, LX125, LX150, FLY, LB, Liberty125, ZIP100, Hiper50, GTS125, GTS250, GTS300, GT200, Sprint, 946, Medley, Primavera etc |
| others | VTC VALVE, FCC CLUTCH, CHINAMFG DRIVE BELT, CHINAMFG injector |
Company Information:
Exhibition Show:
We attend professional motorcycle parts trade fair to promote our products. A great many of customers would come to our booth, show interest in our products and are willing to try our products. Trial order to test quality is warmly welcomed too!
Certificate:
Warehouse:
Packaging & Shipping:
Our Services:
FAQ:
Contact us:
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 3 Months |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | Within Seven Days of Taking Delivery |
| Type: | Drive Face |
| Certification: | ISO9001:2001 |
| Transport Package: | Neutral Packing |
| Trademark: | XY |
| Samples: |
US$ 13/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are there different types of drive pulleys, and how do they differ in their applications?
Yes, there are different types of drive pulleys available, each designed for specific applications based on factors such as power requirements, belt type, speed, and environmental conditions. These different types of drive pulleys offer variations in design, construction, and features to suit various industrial applications. Here’s an overview of some common types of drive pulleys and how they differ in their applications:
1. Flat Belt Pulleys:
Flat belt pulleys have a flat cylindrical surface and are typically used with flat belts. They are commonly found in applications where moderate power transmission is required, such as in light-duty machinery, conveyor systems, and agricultural equipment. Flat belt pulleys are known for their simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and ease of installation. They are available in various sizes and materials, including cast iron, steel, and aluminum.
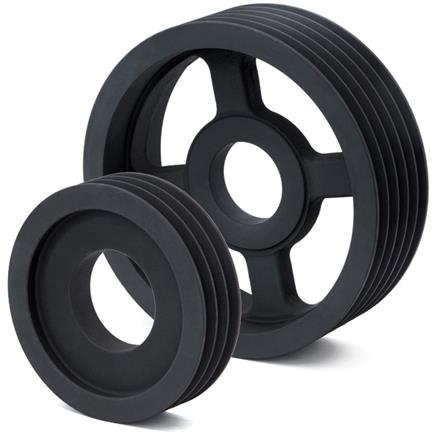
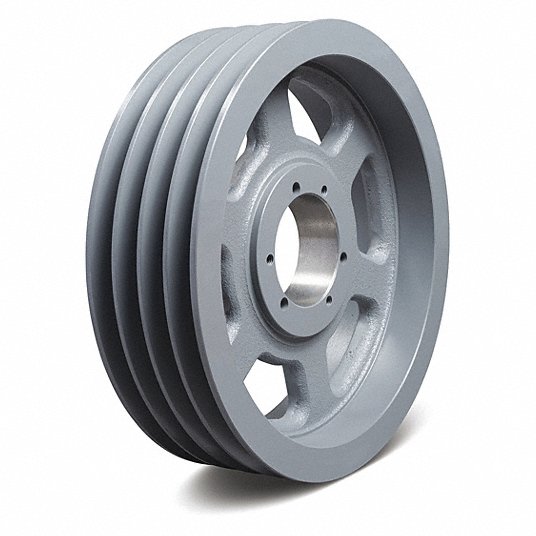
2. V-Belt Pulleys:
V-belt pulleys have a V-shaped groove on their cylindrical surface and are designed to work with V-belts. The V-groove helps improve belt grip and prevents slippage, making them suitable for high-power transmission applications. V-belt pulleys are commonly used in automotive engines, industrial machinery, HVAC systems, and heavy-duty equipment. They are available in different configurations, including single-groove, multi-groove, and variable speed pulleys.
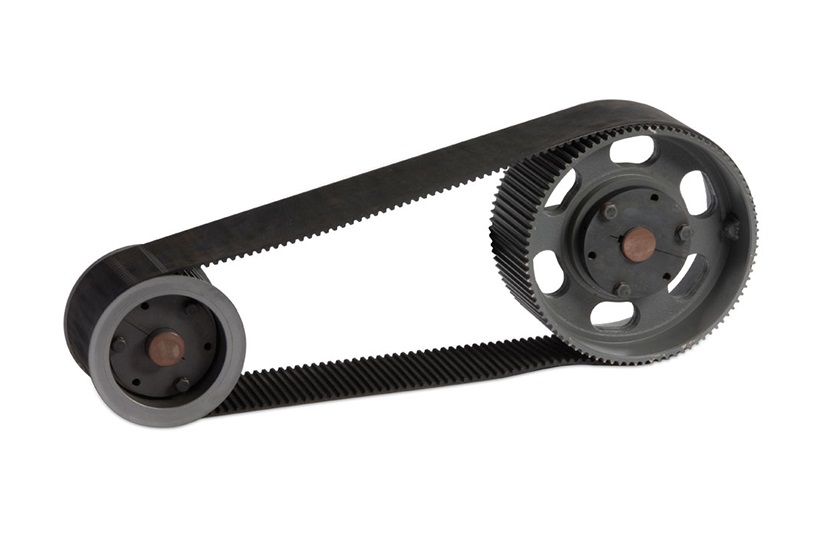
3. Timing Belt Pulleys:
Timing belt pulleys are designed to work with timing belts, also known as synchronous belts. These pulleys have teeth or grooves on their surface that mesh with corresponding teeth on the timing belt, providing precise and synchronous power transmission. Timing belt pulleys are commonly used in applications that require accurate positioning and synchronization of components, such as CNC machines, robotics, printing presses, and automotive engine systems.
4. Chain Drive Sprockets:
Chain drive sprockets are used in systems that utilize roller chains for power transmission. These pulleys have teeth or cogs that mesh with the links of the roller chain, enabling efficient power transfer. Chain drive sprockets are commonly used in heavy-duty applications, such as industrial machinery, conveyors, motorcycles, bicycles, and agricultural equipment. They are available in various configurations, including single-strand, double-strand, and multi-strand sprockets.
5. Cone Pulleys:
Cone pulleys have a tapered or conical shape and are used in applications that require variable speed drives. By adjusting the position of the belt on the conical surface, the effective pulley diameter changes, resulting in different speeds. Cone pulleys are commonly found in machine tools, drill presses, lathes, and other equipment where variable speed control is necessary.
6. Magnetic Pulleys:
Magnetic pulleys are designed with a magnetic surface to attract and hold ferrous materials. They are used in applications such as magnetic separators, material handling systems, recycling, and mining industries. Magnetic pulleys are effective in removing tramp iron or unwanted metal contaminants from conveyed materials.
These are just a few examples of the different types of drive pulleys available. Each type has its own specific design and features that make it suitable for particular applications based on factors like power transmission requirements, belt compatibility, speed control, and environmental conditions. It’s important to select the appropriate type of drive pulley based on the specific needs and operating conditions of the application to ensure optimal performance and longevity.

What maintenance procedures are necessary to ensure the reliability of drive pulleys?
Proper maintenance procedures are essential to ensure the reliability and longevity of drive pulleys. Regular maintenance helps identify and address potential issues before they escalate, minimizing downtime and preventing costly breakdowns. Here are some important maintenance procedures for drive pulleys:
1. Visual Inspection:
Perform regular visual inspections of the drive pulleys to check for any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Look for cracks, chips, or excessive wear on the pulley surface. Inspect the pulley hub and keyway for any signs of damage or corrosion. Ensure that the pulley is properly aligned with the drive shaft and other components. If any abnormalities are detected, further investigation or corrective action may be necessary.
2. Lubrication:
Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for lubrication to ensure smooth operation of the drive pulley. Lubrication reduces friction and heat, preventing premature wear and extending the pulley’s lifespan. Apply the recommended lubricant to the pulley bearings or bushings as per the specified intervals. Ensure that the lubricant used is compatible with the pulley material and operating conditions.
3. Tension and Belt/Chain Alignment:
Check the tension of the belts or chains connected to the drive pulley regularly. Incorrect belt or chain tension can lead to slippage, reduced power transmission efficiency, and accelerated wear on the pulley and associated components. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines or consult the equipment manual for the appropriate tensioning procedures. Additionally, ensure proper alignment between the pulley and the driven components to prevent excessive side loading or belt/chain misalignment.
4. Cleaning:
Keep the drive pulleys clean and free from debris, dust, or contaminants. Regularly remove any accumulated dirt, debris, or residue from the pulley surfaces and grooves. Use appropriate cleaning methods and tools, such as brushes or compressed air, to ensure thorough cleaning without causing damage to the pulley or its components. Clean pulleys help maintain proper belt traction and reduce the risk of slippage.
5. Belt/Chain Maintenance:
In addition to maintaining the drive pulleys, proper maintenance of the belts or chains connected to the pulleys is crucial. Inspect the belts or chains for signs of wear, damage, or stretching. Replace worn-out or damaged belts or chains promptly to prevent adverse effects on the drive pulley’s performance. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for belt or chain tensioning, alignment, and replacement intervals.
6. Balancing:
Imbalance in the drive pulley can result in vibration, increased stress on the pulley and associated components, and reduced overall system performance. Periodically check the balance of the drive pulley and take corrective measures if necessary. Balancing may involve the use of specialized equipment or consulting a professional service provider to ensure proper balancing and smooth operation.
7. Record-Keeping:
Maintain accurate records of maintenance activities performed on the drive pulleys. This includes recording inspection dates, lubrication schedules, belt or chain replacements, and any corrective actions taken. Proper record-keeping helps track maintenance history, identify recurring issues, and ensure compliance with maintenance schedules and recommendations.
8. Professional Inspection:
Consider engaging a qualified professional or a service provider for periodic inspections and maintenance of drive pulleys, especially in complex or critical applications. Professionals can perform more detailed assessments, identify potential issues, and provide expert recommendations to ensure the reliability and optimal performance of the drive pulleys.
In conclusion, regular maintenance procedures are necessary to ensure the reliability of drive pulleys. Visual inspections, proper lubrication, tension and alignment checks, cleaning, belt/chain maintenance, balancing, record-keeping, and professional inspections all contribute to the longevity and optimal operation of drive pulleys, reducing the risk of failures and improving overall system reliability.

Can you explain the key components and design features of a drive pulley?
A drive pulley consists of several key components and design features that enable its proper functioning and efficient power transmission. Understanding these components and design features is essential for the effective selection and utilization of drive pulleys. Here are the main components and design features of a drive pulley:
1. Pulley Body:
The pulley body is the main structure of the drive pulley. It is typically a cylindrical or disk-like component that provides the foundation for the other components. The pulley body is usually made of materials such as steel, cast iron, or aluminum, chosen for their strength, durability, and resistance to wear and corrosion. The body is designed to withstand the forces and stresses encountered during operation.
2. Pulley Rim:
The pulley rim is the outer edge of the drive pulley, and it is where the belt or chain makes contact. The rim is often larger in diameter than the central portion of the pulley to provide a surface for the belt or chain to ride on. It is designed with a specific profile, such as a V-groove or a flat surface, depending on the type of belt or chain being used. The rim’s shape and surface ensure proper engagement and grip, preventing slippage and ensuring efficient power transfer.
3. Hub or Bore:
The hub or bore is the central opening in the drive pulley that allows it to be mounted on a shaft. The hub is typically cylindrical in shape and is sized to fit the diameter of the shaft. It may have keyways, splines, or other features to provide a secure connection with the shaft and prevent slippage. The hub is often secured to the shaft using fasteners such as set screws, keyways, or locking mechanisms.
4. Keyway and Key:
Many drive pulleys have a keyway and key arrangement to ensure a secure and non-slip connection with the shaft. The keyway is a slot cut into the pulley’s bore, while the key is a rectangular metal piece that fits into the keyway. The key prevents relative rotation between the pulley and the shaft, ensuring that the rotational motion is effectively transferred. The keyway and key mechanism provide a strong and reliable connection, especially in applications with high torque or heavy loads.
5. Balancing Features:
Drive pulleys are often balanced to minimize vibration and ensure smooth operation. Imbalances in the pulley can lead to increased wear, noise, and reduced efficiency. Balancing features, such as counterweights or precision machining, are incorporated into the pulley design to achieve proper balance. This helps to maintain the stability and long-term performance of the drive pulley and the entire mechanical system.
6. Flanges and Guards:
In some applications, drive pulleys are equipped with flanges or guards. Flanges are raised edges located on either side of the pulley rim to prevent the belt or chain from slipping off during operation. Flanges help maintain the belt’s alignment and ensure proper engagement with the pulley. Guards, on the other hand, are protective covers that enclose the pulley, preventing contact with moving parts and enhancing safety in the surrounding environment.
7. Surface Coatings and Treatments:
Drive pulleys may undergo surface coatings or treatments to enhance their performance and longevity. These coatings can include materials such as rubber, polyurethane, or ceramic, which provide improved grip, wear resistance, and reduced friction between the pulley and the belt or chain. Surface treatments can also include processes like heat treatment or hardening to increase the pulley’s hardness and durability, particularly in demanding applications.
These are the key components and design features of a drive pulley. By considering these factors and selecting the appropriate pulley design for a specific application, engineers and designers can ensure optimal power transmission, reliability, and longevity in mechanical systems.


editor by CX
2024-05-03